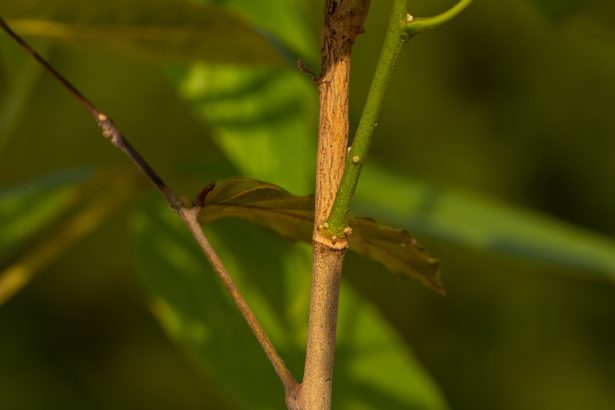
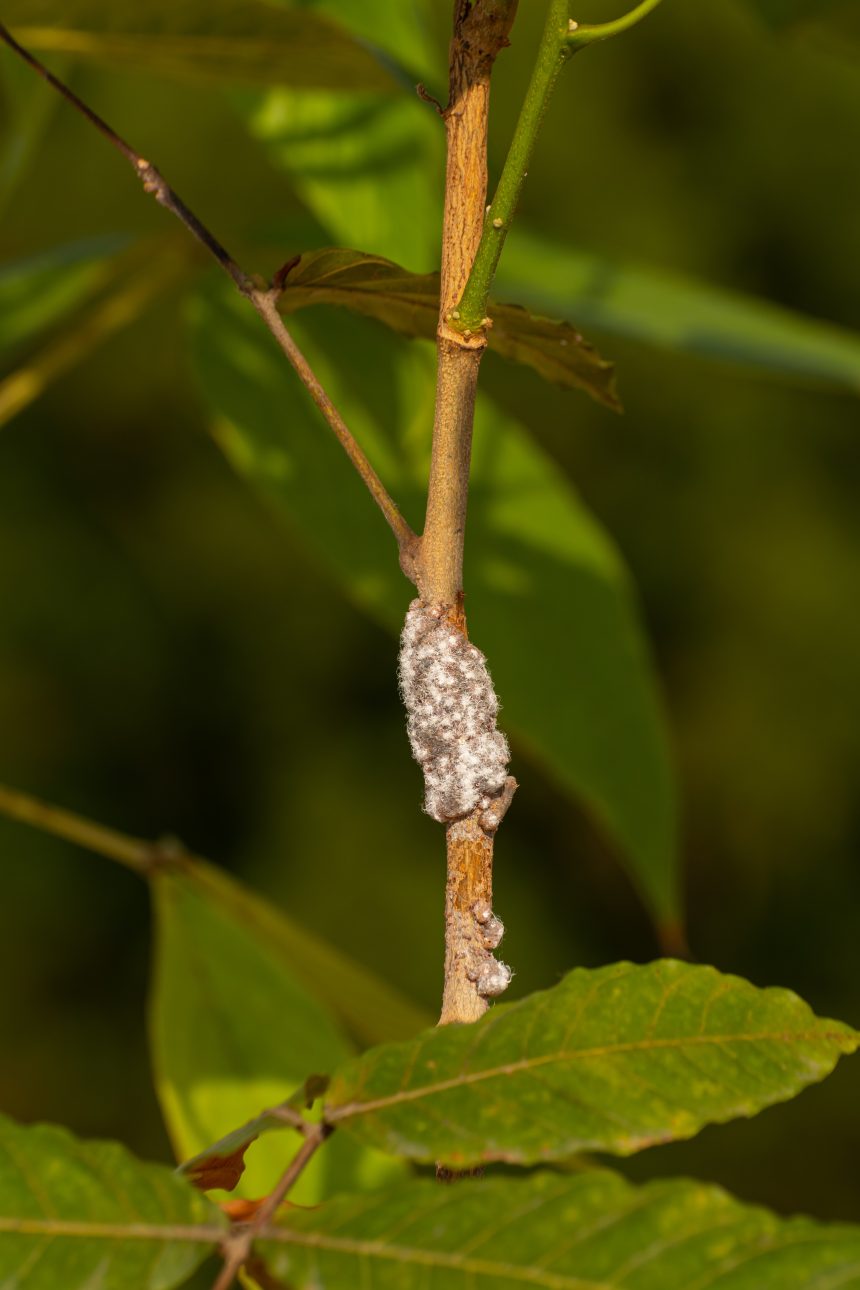
A fungal origin for coveted lac pigment
The colourful pigment extracted from the lac insect may actually be produced by a symbiotic yeast-like organism living inside the…
Fast Four Quiz: Precision Medicine in Cancer
Nuisance Seaweed Found to Produce Compounds with Biomedical Potential
A seaweed considered a threat to the healthy growth of coral reefs…
Bacteria ‘nanowires’ could help scientists develop green electronics
Engineered protein filaments originally produced by bacteria have been modified by scientists…
MIT engineers design tiny batteries for powering cell-sized robots
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots…
5 effective ways to get better sleep
The inability to get a good nights sleep can result in a series of ailments…
WILL COVID-19 EVENTUALLY BECOME JUST A SEASONAL NUISANCE?
Within the next decade, the novel coronavirus responsible for COVID-19 could become little more than a nuisance, causing no more…
Sign Up for Free
Subscribe to our newsletter and don't miss out on our programs, webinars and trainings.
Retired stars join the young stars’ party in the sky: how evolved stars contribute to the early heating of Earth
Researchers from the University of Sheffield and Imperial College London have spotted a ‘retired’ Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) star passing…
Your one-stop resource for medical news and education.
Nuisance Seaweed Found to Produce Compounds with Biomedical Potential
A seaweed considered a threat to the healthy growth of coral reefs in Hawaii may possess the ability to produce…
Nuisance Seaweed Found to Produce Compounds with Biomedical Potential
A seaweed considered a threat to the healthy growth of coral reefs in Hawaii may possess the ability to produce…
New tools used to identify childhood cancer genes
Using a new computational strategy, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have identified 29 genetic…
New 3D printer uses rays of light to shape objects, transform product design
A new 3D printer uses light to transform gooey liquids into complex solid objects in…
Cotton-Based Hybrid Biofuel Cell Could Power Implantable Medical Devices
A glucose-powered biofuel cell that uses electrodes made from cotton fiber could someday help power…
A fungal origin for coveted lac pigment
The colourful pigment extracted from the lac insect may actually be produced by a symbiotic…
Combination approach could overcome treatment resistance in deadly breast cancer
QIMR Berghofer-led research in collaboration with Australian oncology company, Kazia Therapeutics, has found that combining…
Tailored brain stimulation treatment results give new hope for people with depression
Medical researchers at QIMR Berghofer have achieved a significant milestone in the treatment of depression,…
Game-Changer in Emergency Medicine: New AI Test Flags Sepsis Hours Before Symptoms Worsen
When the body's reaction to an infection goes awry, it can result in sepsis, a…
Perfumes and lotions disrupt how body protects itself from indoor air pollutants
Fragrances and lotions don't just change the way people smell, they actively alter the indoor…
Medical Milestone: Surgeons Perform First-Ever Human Bladder Transplant
In a groundbreaking medical achievement, surgeons at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Health…
A Downside of Taurine: It Drives Leukemia Growth
A new scientific study identified taurine, which is made naturally in the body and consumed…
How do therapy dogs help domestic abuse survivors receiving support services?
A new exploration of how therapy dogs can create a safe, nonjudgmental environment for survivors…