Admin
New psychological therapy shows promise in improving quality of life for people living with MND
The largest-ever trial of a psychological intervention for patients with the debilitating neurological condition, conducted by researchers at the University…
Aligned peptide ‘noodles’ could enable lab-grown biological tissues
A team of chemists and bioengineers at Rice University and the University of Houston have achieved a significant milestone in…
AFTER 25 YEARS, RESEARCHERS UNCOVER GENETIC CAUSE OF RARE NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as…
Bacteria ‘nanowires’ could help scientists develop green electronics
Engineered protein filaments originally produced by bacteria have been modified by scientists to conduct electricity. In a study published recently…
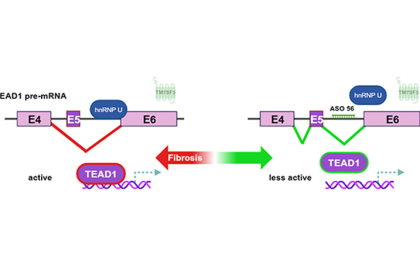
Scientists Discover a New Signaling Pathway and Design a Novel Drug for Liver Fibrosis
A healthy liver filters all the blood in your body, breaks down toxins and digests fats. It produces collagen to…
Advance in immune cell screening uncovers receptors that target prostate cancer
A recent UCLA study demonstrates a new process for screening T cells, part of the body’s natural defenses, for characteristics…
Simulation reveals new mechanism for membrane fusion
An intricate simulation performed by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers using one of the world’s most powerful supercomputers sheds new…
Understanding ‘Y’: Chromosome Discovery Advances Fight Against Heart Failure in Men
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a gene on the Y chromosome that contributes to the greater…