Admin
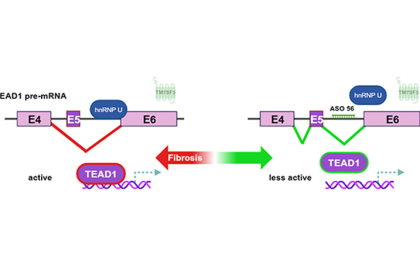
Scientists Discover a New Signaling Pathway and Design a Novel Drug for Liver Fibrosis
A healthy liver filters all the blood in your body, breaks down toxins and digests fats. It produces collagen to…
Advance in immune cell screening uncovers receptors that target prostate cancer
A recent UCLA study demonstrates a new process for screening T cells, part of the body’s natural defenses, for characteristics…
Simulation reveals new mechanism for membrane fusion
An intricate simulation performed by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers using one of the world’s most powerful supercomputers sheds new…
Understanding ‘Y’: Chromosome Discovery Advances Fight Against Heart Failure in Men
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a gene on the Y chromosome that contributes to the greater…
Replacing plastics with alternatives is worse for greenhouse gas emissions in most cases, study finds
Substituting plastics with alternative materials is likely to result in increased GHG emissions, according to research from the University of…
A Deep Dive Into the Genetics of Alcohol Consumption
A research group centered at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine has drilled deep into a dataset…
MIT engineers design flexible “skeletons” for soft, muscle-powered robots
New modular, spring-like devices maximize the work of live muscle fibers so they can be harnessed to power biohybrid bots.…
This 3D printer can figure out how to print with an unknown material
While 3D printing has exploded in popularity, many of the plastic materials these printers use to create objects cannot be…